Device Safe Areas
Overview
Modern iOS and Android mobile devices feature 'safe-area' insets at the top and bottom of the screen. as plugin frames extend to the very top and bottom of the screen, they can overlap with these safe-area insets. If not handled correctly, this overlap can lead to user interface issues within your plugins.
What are Safe Areas?
The concept of 'safe areas' emerged with the widespread adoption of edge-to-edge displays on modern smartphones. These displays allow applications to extend content to the very edges of the screen. These spaces are reserved for system functionality; however, apps can still display backgrounds and content behind them.
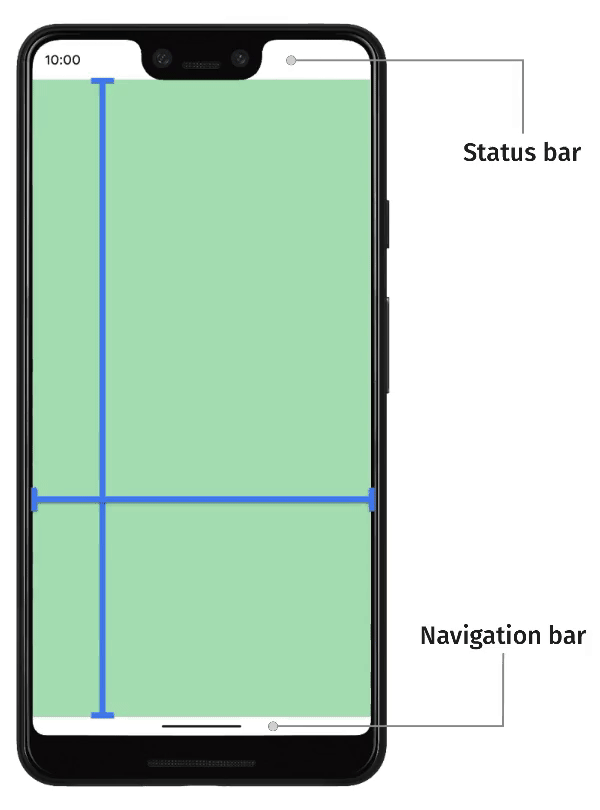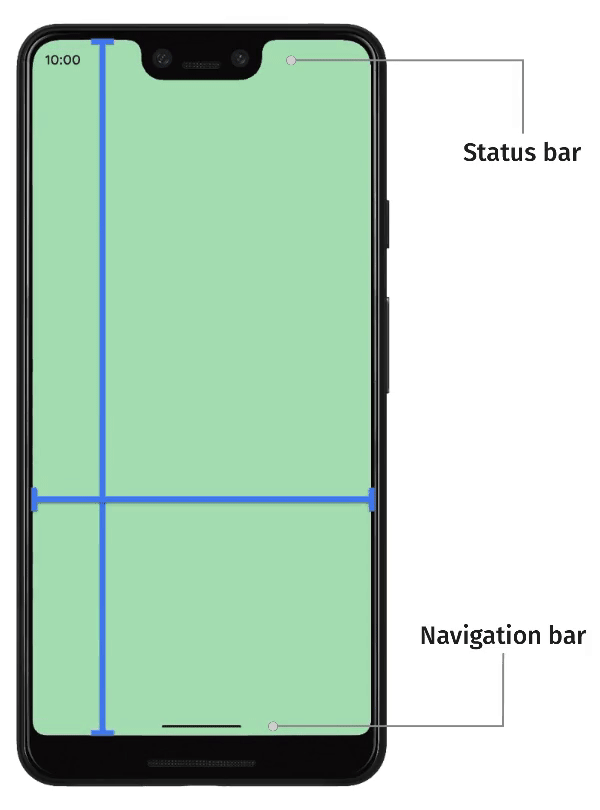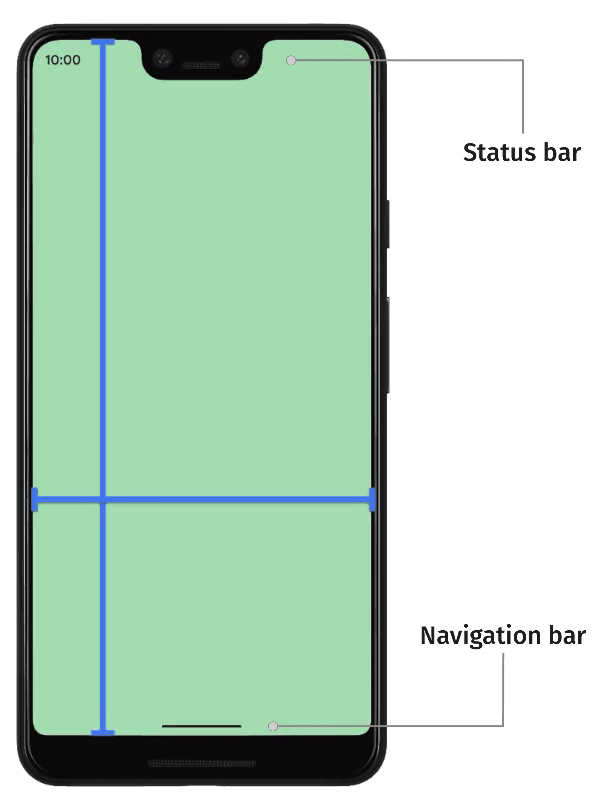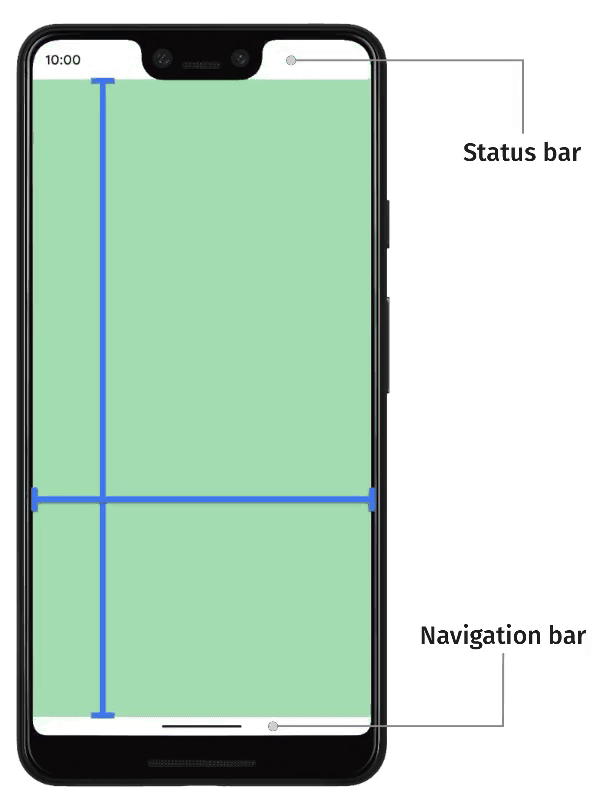
The decision of whether content should render within or outside of safe areas is contextual. For example, scrolling content can be displayed outside of safe areas, provided that users can scroll the first and last items entirely into view within the safe area. This can be achieved by adding padding to the top and bottom of scrolling containers.
CSS [safe-area] Attribute Removal
Please be aware that the injected safe-area="true" attribute is being deprecated and will be completely removed in upcoming releases.
Buildfire previously injected the safe-area attribute to the <html> tag of your plugin's HTML to help you manage safe areas. However, this approach is no longer needed with the introduction of Buildfire custom CSS variables as covered in the following section.
CSS Custom Variables
Buildfire provides a smart custom CSS variables that when the device has a safe area, they will dynamically have the inset value in pixels, otherwise their values will be zero.
Use the following variables in your plugin:
--bf-safe-area-inset-top
--bf-safe-area-inset-bottom
Please be aware that the native CSS environment variables (not prefixed with --bf) safe-area-inset-top and safe-area-inset-bottom are primitive and have known support issues, particularly on Android devices.
To ensure future compatibility, we strongly recommend using the new Buildfire CSS custom variables for handling safe area insets, as detailed in this guide. Failure to update your plugin will result in UI issues on newer devices.
It can be used as follows:
Examples
Examples before and after using Buildfire custom CSS variables:
Without title bar (default launcher behavior):

body {
padding-top: 0;
}

body {
padding-top:
var(--bf-safe-area-inset-top);
}
Scrollable content without navbar:

div:last-of-type {
padding-bottom: 0;
}

div:last-of-type {
padding-bottom:
var(--bf-safe-area-inset-bottom);
}
Fixed bottom content without navbar:
.action-button {
bottom: 0;
}
.action-button {
bottom:
var(--bf-safe-area-inset-bottom);
}
CSS variables will have zero value when not needed;
When the titlebar is visible --bf-safe-area-inset-top will be zero.
When the navbar is visible --bf-safe-area-inset-bottom will be zero.


To display the plugin within the insets boundaries:
body {
padding-top: var(--bf-safe-area-inset-top);
padding-bottom: var(--bf-safe-area-inset-bottom);
}
To adjust the position of an element:
.my-class {
top: calc(5px + var(--bf-safe-area-inset-top));
bottom: calc(10px + var(--bf-safe-area-inset-bottom));
}
To increase the height of an element:
.my-class {
height: calc(<original height> + var(--bf-safe-area-inset-top) + var(--bf-safe-area-inset-bottom));
}
HTML Attributes Injection
Buildfire automatically injects the following attributes to the <html> tag of your plugin's HTML:
titlebar-visible will be automatically injected and removed based on the visibility of the app title bar.
navbar-visible will be automatically injected and removed based on the visibility of the app nav bar.